Hackers, malware, spyware, and ransomware are just a few of the threats facing businesses today. Regardless of the size of your business, high-quality cyber security is a must for anyone with dealings online. And let's face it, whose business isn’t on the internet?
Forms of Cyber Security
1. Firewalls & Antivirus Software
Often used as a first line of defence, and for many online users, the only line of defence, firewalls and antivirus software help stop the malicious software and viruses from infecting your computer. While these are excellent tools, the defence system is often created for known viruses and malicious software. Unfortunately, cyber criminals or “hackers”, are constantly finding new ways to infect computer systems and steal information. That is why regularly updated protective measures are great, but they do not provide 100% protection against all threats.
2. Passwords: The Original Cyber Security
Passwords have been used as cyber security for more than 30 years. They are, most often, alphanumeric codes that are chosen by the user. A password is sometimes personal, be it significant numbers and/or words. More users are opting to use computer generated passwords that are a random succession of numbers, letters (both upper and lower case), and symbols, as this adheres to the parameters that most sites now require when setting up a new account. Unfortunately, far too often, users make one of the following mistakes:
Reusing the Same Password
Do not do this. Yes, it’s tough to remember many different passwords, but if someone steals your password, they are likely to run that same password through all of your accounts, and they will now gain access to anything using that password.
Easily Guessed Passwords
Surprisingly, people still use passwords such as 123456, 11111111, ABCDEFG, QWERTY, and yep, you guessed it, PASSWORD. These are the easiest passwords to guess, and cyber attackers can easily write some code that will run a password check on all of these, plus a number of others.
So… what’s the best type of password you can use? It just needs to be unique enough that no one, not even your spouse or best friend could guess it. If you can’t remember them all, there are two ways to save them. One is the keychain, however, if someone has access to your computer and the password to unlock your whole keychain, they now have all your passwords. The most secure and possibly the most archaic, is to write the passwords down on paper and hide the paper. Offline documents are the only thing that is 100% safe from cyber attacks.
3. Two Factor Authentication (2FA)

Two factor authentication (2FA) is used when signing into a website. It's generally an excellent from of cyber security. 2FA requires a secondary method of authentication, beyond your password, to access your account.
There are a few types of 2FA at the moment:
Hardware Tokens
-
a piece of hardware, like a key fob, which is unique to each owner
-
produces a new numeric code every 30 seconds
-
Some can automatically transfer the code when plugged into a USB port
-
Small and easily misplaced
-
Units are costly
SMS Text Message and Voice Based 2FA
-
On-time passcode delivered via text message
-
Okay for low-risk online activity
-
Considered the least secure form of 2FA
-
Vulnerable to interception due to the third party origin of the code
Software Tokens
-
Most popular form of 2FA
-
Software generated, time-based, one-time passcode
-
Can’t be intercepted, due to the origin being on the same device
-
It’s still software, all of which is susceptible to cyber attacks
Push Notifications
-
Easily view and approve or deny access with a single touch
-
Passwordless, no codes to enter, and no additional codes to enter
-
Reduces the opportunity for phishing and unauthorized access
-
Must be on an internet-connected device that can install apps
-
May have to rely on SMS as a backup in poor service areas
The Future of 2FA Cyber Security
The future of 2FA is through biometrics (fingerprints, retina patterns, and facial recognition). Some of which are already being employed today. While these are likely to become the norm as well as the most secure forms of authentication, as they become more widely used, hackers are likely to focus on cracking them, leading us to the next form of security that is yet to be made available to the general public.
4. Set up a VPN (Virtual Private Network)
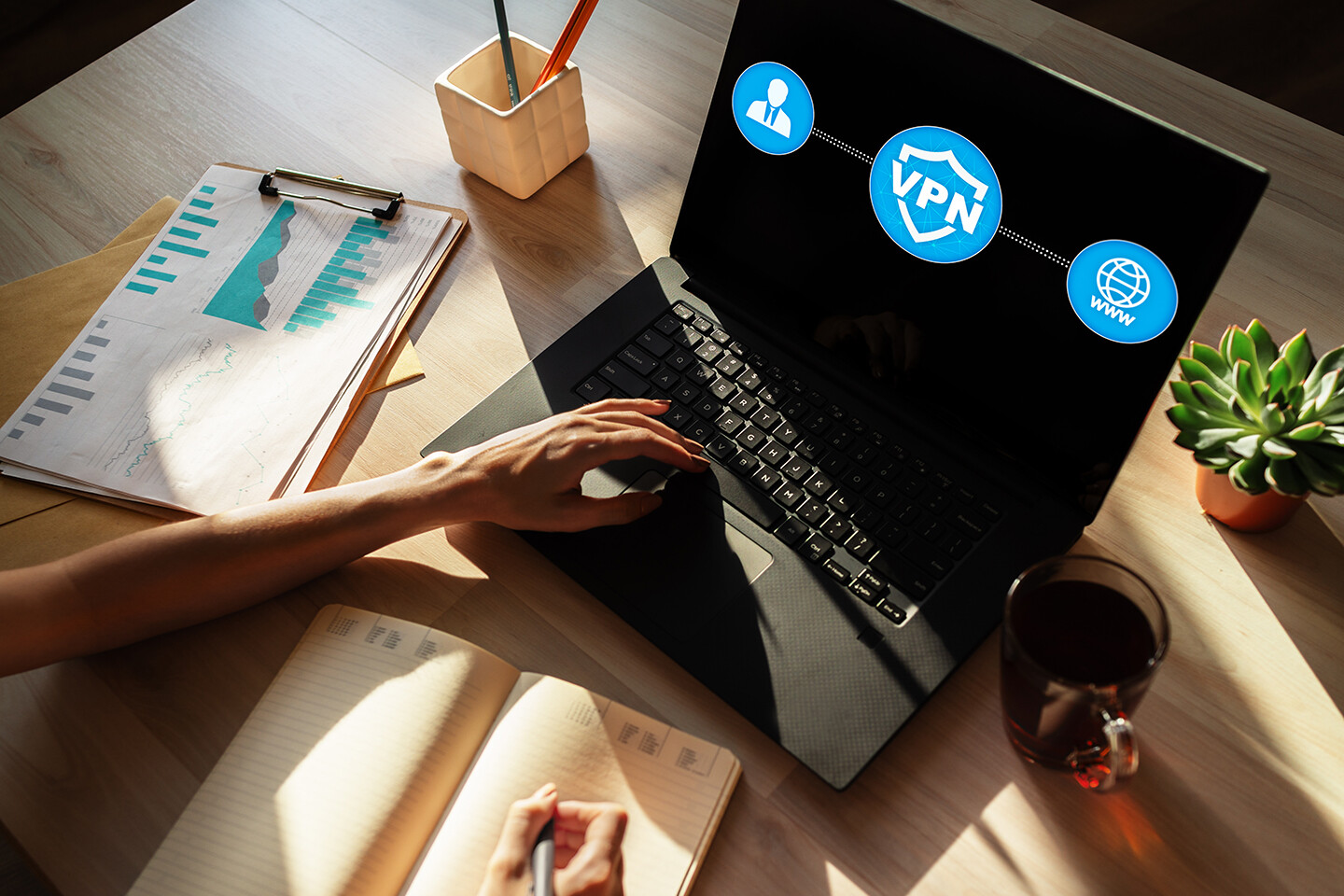

A VPN or Virtual Private Network simply masks your IP address (the numeric address of your network) by assigning it a new, generic one. Therefore, by using a VPN, your network is no longer visible to the world wide web, and you have essentially made your digital presence invisible.
Learn more about the Pros and Cons of using a VPN
Dealing with Ransomware and Malicious Cyber Attacks
Start by staying calm. Cooler heads always prevail. Then, contact your service provider, any external server companies you may deal with, as well as the authorities. Find out exactly what was taken, what the attackers are asking for, and formulate a plan for how you will overcome this unfortunate situation. It won’t be an instant fix, so be patient. But also work diligently to resolve the issue.
Cyber security comes in many forms and how you choose to use it is up to you. After all, you are in charge of protecting yourself and your data from the possible harms that come from cyber attacks.